Aluminium nitride
Its wurtzite phase (w-AlN) has a band gap of ~6 eV at room temperature and has a potential application in optoelectronics operating at deep ultraviolet frequencies.
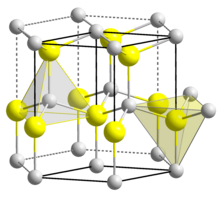
[12] In AlN wurtzite crystal structure, Al and N alternate along the c-axis, and each bond is tetrahedrally coordinated with four atoms per unit cell.
The origin of spontaneous polarization is the strong ionic character of chemical bonds in wurtzite AlN due to the large difference in electronegativity between aluminium and nitrogen atoms.
These polarization effects can be utilized to induce a high density of free carriers at III-nitride semiconductor heterostructure interfaces completely dispensing with the need of intentional doping.
Owing to the broken inversion symmetry along the polar direction, AlN thin film can be grown on either metal-polar or nitrogen-polar faces.
[citation needed] Epitaxially grown thin film crystalline aluminium nitride is used for surface acoustic wave sensors (SAWs) deposited on silicon wafers because of AlN's piezoelectric properties.
Recent advancements in material science have permitted the deposition of piezoelectric AlN films on polymeric substrates, thus enabling the development of flexible SAW devices.
[23] One application is an RF filter, widely used in mobile phones,[24] which is called a thin-film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR).
[25] AlN is also used to build piezoelectric micromachined ultrasonic transducers, which emit and receive ultrasound and which can be used for in-air rangefinding over distances of up to a meter.
AlN buffer layer is a critical building block for AlN-based HEMTs, and it has been grown by using MOCVD or MBE on different substrates.
[32] More researchers are examining the production of light-emitting diodes(LEDs) to operate in the ultraviolet region using aluminium gallium nitride(AlGaN) based semiconductors.