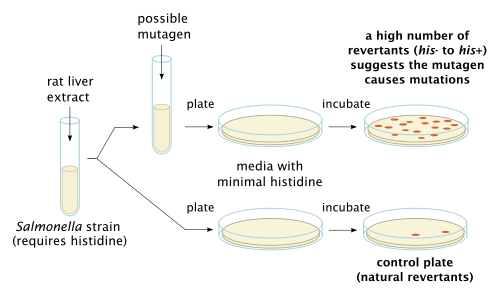
Ames test
[3][4][5][6] The Ames test uses several strains of the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium that carry mutations in genes involved in histidine synthesis.
[9] Examples include tris(2,3-dibromopropyl)phosphate, which was used as a flame retardant in plastic and textiles such as children's sleepwear,[10] and furylfuramide which was used as an antibacterial additive in food in Japan in the 1960s and 1970s.
[15][16] He also cautioned against the "hysteria over tiny traces of chemicals that may or may not cause cancer", that "completely drives out the major risks you should be aware of".
The nitrate compounds may generate nitric oxide, an important signal molecule that can give a false positive.
As with the traditional Ames test, the sample is compared to the natural background rate of reverse mutation in order to establish the genotoxicity of a substance.
The fluctuation method is performed entirely in liquid culture and is scored by counting the number of wells that turn yellow from purple in 96-well or 384-well microplates.
In the more scaled-down 384-well plate microfluctuation method the frequency of mutation is counted as the number of wells out of 48 which have changed color after 2 days of incubation.
A test sample is assayed across 6 dose levels with concurrent zero-dose (background) and positive controls which all fit into one 384-well plate.
The fluctuation method is comparable to the traditional pour plate method in terms of sensitivity and accuracy, however, it does have a number of advantages: it needs less test sample, it has a simple colorimetric endpoint, counting the number of positive wells out of possible 96 or 48 wells is much less time-consuming than counting individual colonies on an agar plate.
Most kits have consumable components in a ready-to-use state, including lyophilized bacteria, and tests can be performed using multichannel pipettes.
The fluctuation method also allows for testing higher volumes of aqueous samples (up to 75% v/v), increasing the sensitivity and extending its application to low-level environmental mutagens.