Amino acid neurotransmitter
An amino acid neurotransmitter is an amino acid which is able to transmit a nerve message across a synapse.
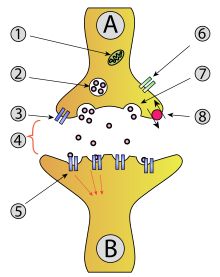
Neurotransmitters (chemicals) are packaged into vesicles that cluster beneath the axon terminal membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse in a process called endocytosis.
[1] Amino acid neurotransmitter release (exocytosis) is dependent upon calcium Ca2+ and is a presynaptic response.
Excitatory amino acids (EAA) will activate post-synaptic cells.
[2] inhibitory amino acids (IAA) depress the activity of post-synaptic cells.