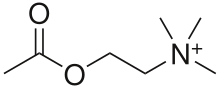
Cholinesterase inhibitor
[4][5] Side effects when used as drugs may include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, loose stools, vivid dreams at night, dehydration, rash, bradycardia, peptic ulcer disease, seizures, weight loss, rhinorrhea, salivation, muscle cramps, and fasciculations.
Since November 2019 the group of ACheIs known as Novichoks have been banned as agents of warfare under the Chemical Weapons Convention.
[6] It is difficult to determine which ChEI has greater efficacy, due to design flaws in head-to-head comparison studies.
[12] Neostigmine is used in combination with a muscarinic antagonist to reverse the effects of non-depolarizing muscle relaxants e.g. rocuronium bromide Common side effects of one ChEI include insomnia, nausea and vomiting, accidental injury, headache, dizziness, bradycardia, hypotension, ecchymosis, and sleep disturbance.
[14][11][7] In 2015, the United States Food and Drug Administration's Adverse Event Reporting System database compared rivastigmine to the other ChEI drugs donepezil and galantamine found that rivastigmine was associated with a higher frequency of reports of death as an adverse event.