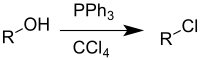
Appel reaction
[3] The use of this reaction is becoming less common, due to carbon tetrachloride being restricted under the Montreal protocol.
A more sustainable version of the Appel reaction has been reported, which uses a catalytic amount of phosphine that is regenerated with oxalyl chloride.
[7] The Appel reaction begins with the formation of the phosphonium salt 3, which is thought to exist as a tight ion pair with 4[8] and therefore is unable to undergo an alpha-elimination to give dichlorocarbene.
The driving force behind this and similar reactions is the formation of the strong PO double bond.
[11] The Appel reaction is also effective on carboxylic acids; this has been used to convert them to oxazolines, oxazines and thiazolines.