Arsenicin A
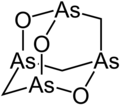
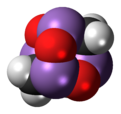
Arsenicin A is a naturally occurring arsenic heterocycle with the molecular formula C3H6As4O3.
It was first isolated from the New Caledonian marine sponge Echinochalina bargibanti.
[1] The compound was characterized by computational and spectroscopic[2][3] techniques and found to possess a cage-like structure similar to adamantane in which the four methanetriyl carbon bridgeheads are replaced by arsenic atoms and three of the six methylene bridges are replaced by oxygen atoms.
[1] Subsequently, the proposed structure was prepared in large quantities via total synthesis and the structure was confirmed by x-ray crystallography.
[5] Arsenicin A is active against promyelocytic leukemia cells at lower concentrations than the arsenic(III) oxide drug Trisenox.