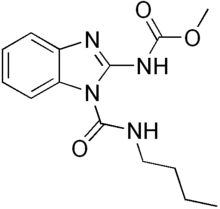
Benzimidazole fungicide
They are applied to cereals, fruits, vegetables and vines, and are also used in postharvest handling of crops.
[2] These fungicides kill cells during mitosis by distorting the mitotic spindle; β-tubulin, a protein important in forming the cytoskeleton, is targeted.
[3] Starting in the late 1960s, they were widely used to control fungal pathogens such as Botrytis cinerea, Cercospora, powdery mildew and eyespot.
[3] Resistant genotypes with certain point mutations were selected.
Because of resistance problems, use of benzimidazole fungicides has declined.