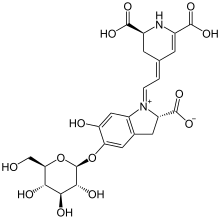
Betanin
Once the pH reaches alkaline levels, betanin degrades by hydrolysis, resulting in a yellow-brown color.
Other dietary sources of betanin and other betalains include the Opuntia cactus, Swiss chard, and the leaves of some strains of amaranth.
Betanin has "not been implicated as causing clinical food allergy when used as a coloring agent".
Its sensitivity to oxygen is highest in products with a high water content and/or containing metal cations (e.g. iron and copper); antioxidants like ascorbic acid and sequestrants can slow this process down, together with suitable packaging.
[1] The panel also concluded that the available toxicological database could not provide data to assign an acceptable daily intake level for beetroot red.