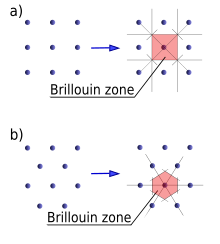
Brillouin zone
The boundaries of this cell are given by planes related to points on the reciprocal lattice.
The importance of the Brillouin zone stems from the description of waves in a periodic medium given by Bloch's theorem, in which it is found that the solutions can be completely characterized by their behavior in a single Brillouin zone.
Another definition is as the set of points in k-space that can be reached from the origin without crossing any Bragg plane.
There are also second, third, etc., Brillouin zones, corresponding to a sequence of disjoint regions (all with the same volume) at increasing distances from the origin, but these are used less frequently.
In general, the n-th Brillouin zone consists of the set of points that can be reached from the origin by crossing exactly n − 1 distinct Bragg planes.