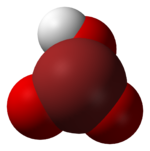
Bromic acid
Bromic acid, also known as hydrogen bromate, is an oxoacid with the molecular formula HBrO3.
[1][2] It is a colorless solution that turns yellow at room temperature as it decomposes to bromine.
[1][3] Bromic acid and bromates are powerful oxidizing agents and are common ingredients in Belousov–Zhabotinsky reactions.
Bromic acid's high instability can be explained because the positively charged hypervalent bromine is connected to the electronegative OH group.
[5][6] The calculated bond lengths are listed below based on three high level theories G2MP2, CCSD(T), and QCISD(T).