Buchner ring expansion
A procedure for preparation of the hazardous starting material needed for carbene generation in the Buchner reaction, ethyl-diazoacetate, is available in Organic Syntheses.
[12] In the procedure provided, Searle includes cautionary instructions due to the highly explosive nature of diazoacetic esters.
[13] The use of rhodium catalysts in the Buchner reaction for carbene generation reduces the number of products by producing predominantly the kinetic cycloheptatrienyl esters.
In the case of electron donating groups, orbital overlap is again possible now in the LUMO, resulting in an increase in antibonding character destabilizing the norcaradiene tautomer.
The importance of the Buchner ring expansion annulation chemistry is evident in the application of this synthetic sequence in the synthesis of biological compounds.
While studying an analogous reaction of carbene addition to thiophene, Stephen Matlin and Lam Chan applied the Buchner ring expansion method in 1981 to generate spiro derivatives of penicillin.
[7] In 1998, Mander et al. synthesized the diterpenoid tropone, harringtonolide[6] using the Buchner intramolecular ring expansion annulation chemistry.
Danheiser et al. utilized intramolecular carbenoid generation to produce substituted azulenes through a Buchner type ring expansion.
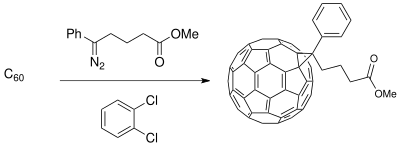
[19] The fullerene compounds can be functionalized for miscibility of C60 to increase efficiency of the solar cell depending upon the polymeric thin film synthesized.
Noels et al. used Rh(II) catalysts for carbene generation under mild reaction conditions (room temperature) to obtain regioselectively the kinetic non-conjugated cycloheptatriene isomer.