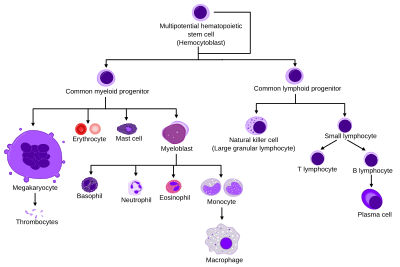
CFU-GEMM
The stem cell will follow a specific lineage depending on the presence of certain growth factors and cytokines.
While present in bone marrow, the place where CFU-GEMM is most common is in the umbilical cord between a mother and baby.
The results of studies conducted by Carow, Hangoc, and Broxmeyer in 1993 reveal that the CFU-GEMM can be classified as a stem cell due to its high replating efficiency in the presence of certain growth factors and cytokines.
[1] The growth and production of CFU-GEMM and BFU-E depend on stimulatory factors from a source of burst-promoting activity (BPA) such as the release of interleukin-1 (IL-1) by monocytes, a has been studied in 1987.
This study revealed that IL-1 plays an important role in the regulation of the production of stimulatory factors that influence the progenitor cells of hematopoiesis.
[7] In another study in 2014, researchers were in search of molecules to stimulate the proliferation of long-term hematopoietic stem cells (LT-HSC).
When used in conjunction with SR1, a known transcription factor, UM171 allowed for suppression of differentiation and led to increased CFU-GEMM growth.