21-Hydroxylase
Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of monooxygenase enzymes that use an iron-containing heme cofactor to oxidize substrates.
In humans, the enzyme is localized in endoplasmic reticulum membranes of cells in adrenal cortex,[14][15] and is encoded by the CYP21A2 gene which is located near the CYP21A1P pseudogene that has high degree of sequence similarity.
Though often thought of as "junk DNA", research has shown that retaining these faulty copies can have a beneficial role, often providing regulation of their parent genes.
[28] MHC class III is the most gene-dense region of the human genome, containing many genes that have, as of 2023 - unknown functions or structures.
[33] The number of RCCX segments varies between one and four in a chromosome,[30] with the prevalence of approximately 15% for monomodular, 75% for bimodular (STK19-C4A-CYP21A1P-TNXA-STK19B-C4B-CYP21A2-TNXB),[31][34] and 10% for trimodular in Europeans.
[30][35] Due to the high degree of homology between the CYP21A2 gene and the CYP21A1P pseudogene and the complexity of the RCCX locus, it is difficult to perform molecular diagnostics for CYP21A2.
The pseudogene can have single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) that are identical or similar to those in the functional gene, making it difficult to distinguish between them.
[38][37] Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) molecular diagnostics uses selective primers to amplify specific segments of the DNA sequence that are relevant for diagnosing or detecting a certain disease or condition.
Moreover, PCR may not be able to detect complex variants such as large gene conversions, deletions, or duplications, which are frequent in the case of the CYP21A2.
This method is time-consuming and requires a large amount of good-quality DNA, which makes it less applicable in routine diagnostic settings.
[42][43][44] Steroid 21-hydroxylase, is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of monooxygenase enzymes, the protein has 494 amino acid residues with a molecular weight of 55,000.
[46] Each subunit in the human enzyme consists of a total of 13 α-helices and 9 β-strands that folds into a triangular prism-like tertiary structure.
[49] The sea lamprey, an early jawless fish species that originated over 500 million years ago, provides valuable insights into the evolution and emergence of Cyp21.
This suggests the presence of a complex and highly specific corticosteroid signaling pathway that emerged at least half a billion years ago during early vertebrate evolution.
[51] Rhesus macaques and orangutans possess two copies of Cyp21, while chimpanzees have three, still, a pseudogene (CYP21A1P) is only present in humans among primates.
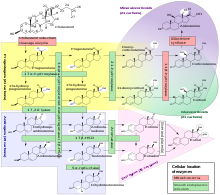
The cytochrome P450 enzymes catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids.
[14] C-H bond breaking to create a primary carbon radical is thought to be the rate-limiting step in the hydroxylation.
[12] Genetic variants in the CYP21A2 gene cause a disturbance in the development of the enzyme, leading to congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
Simple-virilizing CAH patients (~1-2% enzyme function)[58] maintain adequate sodium homeostasis, but exhibit other symptoms shared by the salt-wasting form, including accelerated growth in childhood and ambiguous genitalia in female neonates.
In later life, the signs and symptoms of the condition may include acne, hirsutism, male-pattern baldness, irregular menstruation, and infertility.
A variant of this gene has been reported to cause autosomal dominant posterior polar cataract, suggesting that steroid 21-hydroxylase may be involved in the extra-adrenal biosynthesis of aldosterone and cortisol in the lens of the eye.