Cadmium iodide
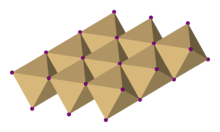
It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects.
[2] Historically, cadmium iodide was used as a catalyst for the Henkel process, a high-temperature isomerisation of dipotassium phthalate to yield the terephthalate.
As existing Bio-PET is still reliant on petroleum as a source of p-xylene, the Henkel process could theoretically offer a completely bioplastic route to polyethylene terephthalate.
Cadmium iodide is mostly ionically bonded but with partial covalent character.
Compounds with any of the following characteristics tend to adopt the CdI2 structure:[citation needed]