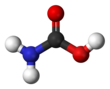
Carbamic acid
The carbamoyl functional group RR′N–C(=O)– (often denoted by Cbm) is the carbamic acid molecule minus the OH part of the carboxyl.
The zwitterionic form H3N+−COO− is very unstable and promptly decomposes into ammonia and carbon dioxide,[6] yet there is a report of its detection in ices irradiated with high-energy protons.
[5] These carbamic acids are generally unstable at room temperature, reverting to the parent amine and carbon dioxide.
[9] Some carbamate esters have use as muscle relaxants, including Emylcamate, Phenprobamate, Styramate and other members of ATC code M03BA.
Hydrolysis of the ester bond then produces a carbamic acid –NHC(=O)OH, which then loses carbon dioxide yielding the desired amine.