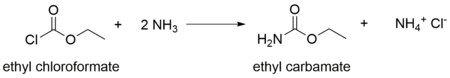
Ethyl carbamate
[citation needed] Prior to World War II, ethyl carbamate saw relatively heavy use in the treatment of multiple myeloma before it was found to be toxic, carcinogenic, and largely ineffective.
[10] One advantage of using ethyl carbamate is that it has a very long duration of action, with some adult rats remaining anaesthetised 24 hours after administration of the drug.
[12] Formerly, ethyl carbamate was used as a chemical intermediate in the preparation of amino resins, that were in turn used as crosslinking agents for permanent-press textile treatments to create "wash-and-wear" fabrics.
[19] Another important mechanism for ethyl carbamate formation in alcoholic beverages is the reaction from cyanide as precursor, which causes comparably high levels in spirits derived from cyanogenic plants, such as rhum agricole.
Acute toxicity studies show that the lowest fatal dose in rats, mice, and rabbits equals 1.2 g/kg or more.
When ethyl carbamate was used medicinally, about 50% of the patients exhibited nausea and vomiting, and long-time use led to gastroenteric hemorrhages.
[24] In 2006, the Liquor Control Board of Ontario in Canada rejected imported cases of sherry due to excessive levels of ethyl carbamate.
Studies in Hong Kong (2009)[25] and Korea (2015)[26] outline the extent of the accumulative exposure to ethyl carbamate in daily life.
There is little doubt[28] that ethyl carbamate in alcoholic beverages is very important to health authorities, while the cumulative daily exposure in the typical diet is also an issue of rising concern that merits closer observation.
On the other hand, the reference method set by the International Organization of Vine and Wine (OIV) uses solid phase extraction (SPE) preceding GC–MS quantification.
Nevertheless, several efforts have also been done to develop new methodologies to determine EC without using long procedures and hard-working analyses, combining precision to high sensitivity.
In this regard, headspace solid phase microextraction (HS-SPME) has been gaining great highlighting and alternative methodologies has been proposed using the most recent identification and quantification technology, such as gas chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry detection (GC–MS/MS) and two-dimensional gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC × GC–ToFMS).