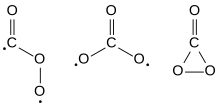
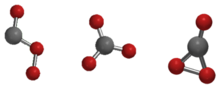
Carbon trioxide
The possible isomers of carbon trioxide include ones with molecular symmetry point groups Cs, D3h, and C2v.
Carbon trioxide can be produced, for example, in the drift zone of a negative corona discharge by reactions between carbon dioxide (CO2) and the atomic oxygen (O) created from molecular oxygen by free electrons in the plasma.
[2] Another reported method is photolysis of ozone O3 dissolved in liquid CO2, or in CO2/SF6 mixtures at −45 °C, irradiated with light of 253.7 nm.
The formation of CO3 is inferred but it appears to decay spontaneously by the route with a lifetime much shorter than 1 minute.
[3] Carbon trioxide can be made by blowing ozone at dry ice (solid CO2), and it has also been detected in reactions between carbon monoxide (CO) and molecular oxygen (O2).