Metal carbonyl
Except vanadium hexacarbonyl, only metals with even atomic number, such as chromium, iron, nickel, and their homologs, build neutral mononuclear complexes.
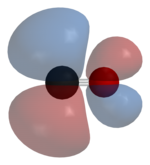
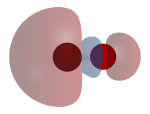
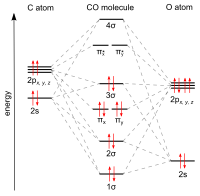
A sigma (σ) bond arises from overlap of the nonbonding (or weakly anti-bonding) sp-hybridized electron pair on carbon with a blend of d-, s-, and p-orbitals on the metal.
For compounds with doubly bridging CO ligands, denoted μ2-CO or often just μ-CO, the bond stretching frequency νCO is usually shifted by 100–200 cm−1 to lower energy compared to the signatures of terminal CO, which are in the region 1800 cm−1.
[citation needed] Most mononuclear carbonyl complexes are colorless or pale yellow, volatile liquids or solids that are flammable and toxic.
Metal carbonyls are soluble in nonpolar and polar organic solvents such as benzene, diethyl ether, acetone, glacial acetic acid, and carbon tetrachloride.
[11] Illustrative of the differing time scales, investigation of dicobalt octacarbonyl (Co2(CO)8) by means of infrared spectroscopy provides 13 νCO bands, far more than expected for a single compound.
[citation needed] Iron pentacarbonyl exhibits only a single 13C NMR signal owing to rapid exchange of the axial and equatorial CO ligands by Berry pseudorotation.
Neutral metal carbonyls can be converted to charged species by derivatization, which enables the use of electrospray ionization (ESI), instrumentation for which is often widely available.
The molar mass of the parent complex can be determined, as well as information about structural rearrangements involving loss of carbonyl ligands under ESI-MS conditions.
[29] Mass spectrometry combined with infrared photodissociation spectroscopy can provide vibrational informations for ionic carbonyl complexes in gas phase.
[30] In the investigation of the infrared spectrum of the Galactic Center of the Milky Way, monoxide vibrations of iron carbonyls in interstellar dust clouds were detected.
It is discussed whether in the reducing hydrothermal environments of the prebiotic prehistory such complexes were formed and could have been available as catalysts for the synthesis of critical biochemical compounds such as pyruvic acid.
[34] Traces of the carbonyls of iron, nickel, and tungsten were found in the gaseous emanations from the sewage sludge of municipal treatment plants.
In the presence of carbon monoxide, cobalt salts are quantitatively converted to the tetracarbonylcobalt(−1) anion:[9] Some metal carbonyls are prepared using CO directly as the reducing agent.
[47] The cationic hexacarbonyl salts of manganese, technetium and rhenium can be prepared from the carbonyl halides under carbon monoxide pressure by reaction with a Lewis acid.
In the "Hieber base reaction", hydroxide ion attacks the CO ligand to give a metallacarboxylic acid, followed by the release of carbon dioxide and the formation of metal hydrides or carbonylmetalates.
Carbonyl iron is used inter alia for the preparation of inductors, pigments, as dietary supplements,[59] in the production of radar-absorbing materials in the stealth technology,[60] and in thermal spraying.
In the oxo process, an alkene, hydrogen gas, and carbon monoxide react together with a catalyst (such as dicobalt octacarbonyl) to give aldehydes.
[62] Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules are metal carbonyl complexes that are being developed as potential drugs to release CO. At low concentrations, CO functions as a vasodilatory and an anti-inflammatory agent.
A special case is CF3NC, an unstable molecule that forms stable complexes whose behavior closely parallels that of the metal carbonyls.
Exposure occurs by inhalation, or for liquid metal carbonyls by ingestion or due to the good fat solubility by skin resorption.
[69] Inhalation of nickel tetracarbonyl causes acute non-specific symptoms similar to a carbon monoxide poisoning, such as nausea, cough, headache, fever, and dizziness.
In addition to pathological alterations of the lung, such as by metalation of the alveoli, damages are observed in the brain, liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, and spleen.
[70] Chronic exposure by inhalation of low concentrations of nickel tetracarbonyl can cause neurological symptoms such as insomnia, headaches, dizziness and memory loss.
[38] The synthesis of the first true heteroleptic metal carbonyl complex was performed by Paul Schützenberger in 1868 by passing chlorine and carbon monoxide over platinum black, where dicarbonyldichloroplatinum (Pt(CO)2Cl2) was formed.
[75] The following year, Mond and Marcellin Berthelot independently discovered iron pentacarbonyl, which is produced by a similar procedure as nickel tetracarbonyl.
Heinrich Hirtz and his colleague M. Dalton Cowap synthesized metal carbonyls of cobalt, molybdenum, ruthenium, and diiron nonacarbonyl.
[citation needed] Walter Hieber played in the years following 1928 a decisive role in the development of metal carbonyl chemistry.
[38] Also in the 1930s Walter Reppe, an industrial chemist and later board member of BASF, discovered a number of homogeneous catalytic processes, such as the hydrocarboxylation, in which olefins or alkynes react with carbon monoxide and water to form products such as unsaturated acids and their derivatives.
BASF built in the 1960s a production facility for acrylic acid by the Reppe process, which was only superseded in 1996 by more modern methods based on the catalytic propylene oxidation.