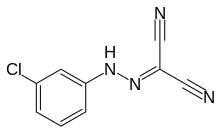
Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone
Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP; also known as [(3-chlorophenyl)hydrazono]malononitrile) is a chemical inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation.
In general, CCCP causes the gradual destruction of living cells and death of the organism,[1][2] although mild doses inducing partial decoupling have been shown to increase median and maximum lifespan in C. elegans models, suggesting a degree of hormesis.
The chemical acts essentially as an ionophore and reduces the ability of ATP synthase to function optimally.
It is routinely[6] used as an experimental uncoupling agent in cell and molecular biology, particularly in the study of mitophagy,[7] where it was integral in discovering the role of the Parkinson's disease-associated ubiquitin ligase Parkin.
[7] Outside of its effects on mitochondria, CCCP may also disrupt lysosomal degradation during autophagy.