Cardiology
[citation needed] Per Doximity, adult cardiologists earn an average of $436,849 per year in the U.S.[5] Cardiac electrophysiology is the science of elucidating, diagnosing, and treating the electrical activities of the heart.
The term is usually used to describe studies of such phenomena by invasive (intracardiac) catheter recording of spontaneous activity as well as of cardiac responses to programmed electrical stimulation (PES).
[6][7] The cardiac electrophysiology study typically measures the response of the injured or cardiomyopathic myocardium to PES on specific pharmacological regimens in order to assess the likelihood that the regimen will successfully prevent potentially fatal sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF) in the future.
Sometimes a series of electrophysiology-study drug trials must be conducted to enable the cardiologist to select the one regimen for long-term treatment that best prevents or slows the development of VT or VF following PES.
[6] Clinical cardiac electrophysiology is a branch of the medical specialty of cardiology and is concerned with the study and treatment of rhythm disorders of the heart.
Electrophysiologists work closely with other cardiologists and cardiac surgeons to assist or guide therapy for heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias).
[10][11] Vascular disorders such as atherosclerosis and peripheral arterial disease cause significant morbidity and mortality in aged people.
Transesophageal echo provides higher spatial resolution than trans thoracic echocardiography and because the probe is located in the esophagus, it is not limited by attenuation due to anterior chest structures such as the ribs, chest wall, breasts, lungs that can hinder the quality of trans thoracic echocardiography.
[14] Cardiac MRI utilizes special protocols to image heart structure and function with specific sequences for certain diseases such as hemochromatosis and amyloidosis.
Cardiac CT utilizes special protocols to image heart structure and function with particular emphasis on coronary arteries.
[15] A large number of procedures can be performed on the heart by catheterization, including angiogram, angioplasty, atherectomy, and stent implantation.
The main advantages of using the interventional cardiology or radiology approach are the avoidance of the scars and pain, and long post-operative recovery.
Additionally, interventional cardiology procedure of primary angioplasty is now the gold standard of care for an acute myocardial infarction.
In recent times, the focus is gradually shifting to preventive cardiology due to increased cardiovascular disease burden at an early age.
Preventive cardiology also deals with routine preventive checkup though noninvasive tests, specifically electrocardiography, fasegraphy, stress tests, lipid profile and general physical examination to detect any cardiovascular diseases at an early age, while cardiac rehabilitation is the upcoming branch of cardiology which helps a person regain their overall strength and live a normal life after a cardiovascular event.
She worked with Alfred Blalock and Vivien Thomas at the Johns Hopkins Hospital where they experimented with dogs to look at how they would attempt to surgically cure these "blue babies".
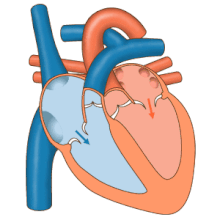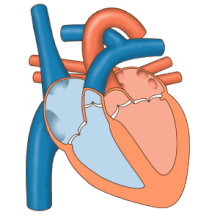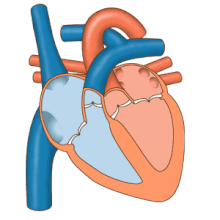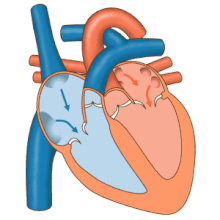
The electrical system of the heart is centered on the periodic contraction (squeezing) of the muscle cells that is caused by the cardiac pacemaker located in the sinoatrial node.
Dysfunction of the electrical system manifests in many ways and may include Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome, ventricular fibrillation, and heart block.
These arteries, when healthy, are capable of autoregulation to maintain coronary blood flow at levels appropriate to the needs of the heart muscle.
These relatively narrow vessels are commonly affected by atherosclerosis and can become blocked, causing angina or myocardial infarction (a.k.a., a heart attack).
[26] A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw.
[36][37] In those with stable CAD it is unclear if PCI or CABG in addition to the other treatments improve life expectancy or decreases heart attack risk.
Those who have severe symptoms from an arrhythmia may receive urgent treatment with a jolt of electricity in the form of cardioversion or defibrillation.
Less common causes include major blood loss, lack of oxygen, very low potassium, heart failure, and intense physical exercise.
[71] Lifestyle changes include weight loss, decreased salt intake, physical exercise, and a healthy diet.
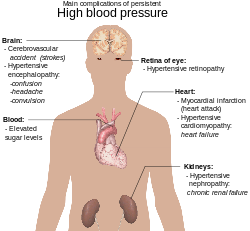
[66] The treatment of moderate to severe high arterial blood pressure (defined as >160/100 mmHg) with medication is associated with an improved life expectancy and reduced morbidity.
[99] When present they may include rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, and feeling tired.
[102] Certain cases may be due to infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother.
Also, a balloon atrial septostomy can be done to relieve hypoxemia caused by DORV with the Taussig-Bing anomaly while surgical correction is awaited.
[citation needed] Cardiology is known for randomized controlled trials that guide clinical treatment of cardiac diseases.