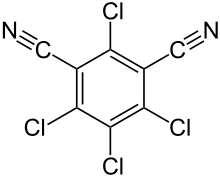
Chlorothalonil
Chlorothalonil (2,4,5,6-tetrachloroisophthalonitrile) is an organic compound mainly used as a broad spectrum, nonsystemic fungicide, with other uses as a wood protectant, pesticide, acaricide, and to control mold, mildew, bacteria, algae.
It is applied as a dust, dry or water-soluble grains, a wettable powder, a liquid spray, a fog, and a dip.
For skin contact and ingestion, chlorothalonil is rated toxicity category IV, "practically nontoxic", meaning the oral and dermal LD50 is greater than 10,000 mg/kg.
[8] Common chlorothalonil synthesis procedures frequently result in contamination of it with small amounts of hexachlorobenzene (HCB), which is toxic.
[2] In 2019, a review of the evidence found that "a high risk to amphibians and fish was identified for all representative uses", and that chlorothalonil breakdown products may cause DNA damage.
[15] In March 2019, as a result of the previously mentioned research, the European Union banned the use of chlorothalonil[13] dated to take effect May 20, 2020.
[17] Chlorothalonil can be produced by the direct chlorination of isophthalonitrile or by dehydration of tetrachloroisophthaloyl amide with phosphoryl chloride.
[7] Technical grade chlorothalonil contains traces of dioxins and hexachlorobenzene,[2] a persistent organic pollutant banned under the Stockholm Convention.