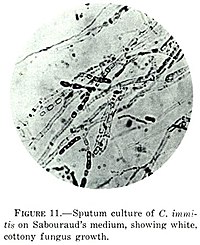
Coccidioides immitis
Coccidioides immitis is a pathogenic fungus that resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, northern Mexico, and a few other areas in the Western Hemisphere.
are found in alkaline, sandy soils from semi-desert regions with hot summers, gentle winters, and annual rainfall between 10 and 50 centimetres (3.9 and 19.7 in).
However, because the Coccidioides creates a mass that can mimic a lung tumor, the correct diagnosis may require a tissue sample (biopsy).
Nevertheless, although it was initially used in the long-term treatment of nonmeningeal extrapulmonary disease, more-potent, less-toxic triazoles (fluconazole and itraconazole) have replaced it.
Itraconazole (400 mg/day) appears to have efficacy equal to that of fluconazole in the treatment of nonmeningeal infection and have the same relapse rate after therapy is discontinued.
In a case report of a 23-year-old Black male with HIV and coccidioidal meningitis, combination therapy of amphotericin B and posaconazole led to clinical improvement.
A published report described a patient with disseminated and meningeal coccidioidomycosis in whom conventional therapy with fluconazole, voriconazole, and amphotericin B failed; caspofungin 50 mg/day after a loading dose of 70 mg intravenously was also unsuccessful.
The objectives of treatment are resolution of infection, decrease of antibody titers, return of function of involved organs, and prevention of relapse.
Therapy is tailored based on a combination of resolution of symptoms, regression of radiographic abnormalities, and changes in CF IgG titers.
Along with C. posadasii, C. immitis was featured on the select agents and toxins list compiled by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), as evident from the Code of Federal Regulations (42 CFR 73).
[15] However, on October 5, 2012 due to advances in medical research and development of a number of licensed treatments, both pathogens were removed from the HHS select agents listing.