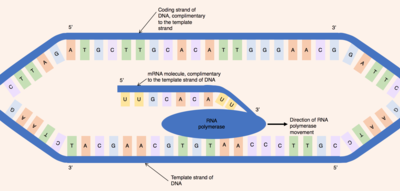
Coding strand
The DNA double helix is rewound by RNA polymerase at the rear of the transcription bubble.
[3] Like how two adjacent zippers work, when pulled together, they unzip and rezip as they proceed in a particular direction.
Various factors can cause double-stranded DNA to break; thus, reorder genes or cause cell death.
[4] Where the helix is unwound, the coding strand consists of unpaired bases, while the template strand consists of an RNA:DNA composite, followed by a number of unpaired bases at the rear.
This hybrid consists of the most recently added nucleotides of the RNA transcript, complementary base-paired to the template strand.