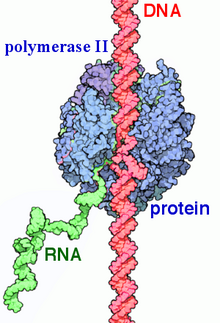
RNA polymerase II
The technique separated the enzymes by the order of the corresponding elutions, Ι,ΙΙ,ΙΙΙ, by increasing the concentration of ammonium sulfate.
Various studies has shown that disruption of transcription elongation is implicated in cancer, neurodegeneration, HIV latency etc.
[10] The purified enzyme has typically 10–12 subunits (12 in humans and yeast) and is incapable of specific promoter recognition.
The theoretical maximum for the specificity constant is the diffusion limit of about 108 to 109 (M−1s−1), where every collision of the enzyme with its substrate results in catalysis.
[24][25] This pausing is especially pronounced at nucleosomes, and arises in part through the polymerase entering a transcriptionally incompetent backtracked state.
Alpha-Amanitin inhibits RNAP II by strong interactions in the enzyme's "funnel", "cleft", and the key "bridge α-helix" regions of the RPB-1 subunit.
This is an outline of an example mechanism of yeast cells by which chromatin structure and histone post-translational modification help regulate and record the transcription of genes by RNA polymerase II.
This pathway gives examples of regulation at these points of transcription: This refers to various stages of the process as regulatory steps.
The carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II typically consists of up to 52 repeats of the sequence Tyr-Ser-Pro-Thr-Ser-Pro-Ser.
The form polymerase IIA joins the preinitiation complex, this is suggested because IIA binds with higher affinity to the TBP (TATA-box binding protein), the subunit of the general transcription factor TFIID, than polymerase IIO form.
Once the domain is completely dephosphorylated the RNAP II enzyme is "recycled" and catalyzes the same process with another initiation site.
[33] Oxidative DNA damage may block RNA polymerase II transcription and cause strand breaks.
It appears that transcription is coupled to repair of DNA double-strand breaks by RNA templated homologous recombination.
This repair process efficiently and accurately rejoins double-strand breaks in genes being actively transcribed by RNA polymerase II.