Conjugated protein
Conjugated proteins are classified on the basis of the chemical nature of their prosthetic groups.
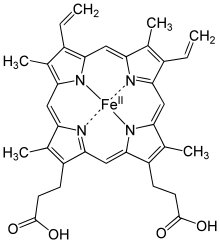
Some examples of conjugated proteins are lipoproteins, glycoproteins, Nucleoproteins, phosphoproteins, hemoproteins, flavoproteins, metalloproteins, phytochromes, cytochromes, opsins, and chromoproteins.
They range from glycoproteins in cell surface membranes that constitute the glycocalyx, to important antibodies produced by leukocytes.
Chemical synthesized polysaccharide–protein conjugates been used for food industry, vaccines, and drug delivery systems.
[2] They are promising alternatives to PEG–protein drugs, in which non-biodegradable high molecular weight PEG causes health concerns.