Antibody
[4] To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety.
However, other work indicates that survival niches can readily be established within the mucosal tissues- though the classes of antibodies involved show a different hierarchy from those in the bone marrow.
[15] Durable protection from infections caused by a given microbe – that is, the ability of the microbe to enter the body and begin to replicate (not necessarily to cause disease) – depends on sustained production of large quantities of antibodies, meaning that effective vaccines ideally elicit persistent high levels of antibody, which relies on long-lived plasma cells.
At the same time, many microbes of medical importance have the ability to mutate to escape antibodies elicited by prior infections, and long-lived plasma cells cannot undergo affinity maturation or class switching.
[20] In between them is a hinge region of the heavy chains, whose flexibility allows antibodies to bind to pairs of epitopes at various distances, to form complexes (dimers, trimers, etc.
[41] Upon antigen binding, they cluster in large patches, which can exceed 1 micrometer in diameter, on lipid rafts that isolate the BCRs from most other cell signaling receptors.
The prefix "Ig" stands for immunoglobulin, while the suffix denotes the type of heavy chain the antibody contains: the heavy chain types α (alpha), γ (gamma), δ (delta), ε (epsilon), μ (mu) give rise to IgA, IgG, IgD, IgE, IgM, respectively.
[citation needed] Activated B cells differentiate into either At the prenatal and neonatal stages of life, the presence of antibodies is provided by passive immunization from the mother.
Second, some complement system components form a membrane attack complex to assist antibodies to kill the bacterium directly (bacteriolysis).
[59] These antibodies undergo quality checks in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which contains proteins that assist in proper folding and assembly.
[45] Rejection of xenotransplantated organs is thought to be, in part, the result of natural antibodies circulating in the serum of the recipient binding to α-Gal antigens expressed on the donor tissue.
[62] Although a huge repertoire of different antibodies is generated in a single individual, the number of genes available to make these proteins is limited by the size of the human genome.
[65] The rearrangement of several subgenes (i.e. V2 family) for lambda light chain immunoglobulin is coupled with the activation of microRNA miR-650, which further influences biology of B-cells.
In these rapidly dividing cells, the genes encoding the variable domains of the heavy and light chains undergo a high rate of point mutation, by a process called somatic hypermutation (SHM).
[72][73] The variable domain exon is rejoined through a process called non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) to the desired constant region (γ, α or ε).
[81] For example, in the case of malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum, some antibodies from those who had been infected demonstrated an insertion from chromosome 19 containing a 98-amino acid stretch from leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 1, LAIR1, in the elbow joint.
Von Behring and Kitasato put forward the theory of humoral immunity, proposing that a mediator in serum could react with a foreign antigen.
[93] The next major advance was in the 1940s, when Linus Pauling confirmed the lock-and-key theory proposed by Ehrlich by showing that the interactions between antibodies and antigens depend more on their shape than their chemical composition.
[98] Together, these scientists deduced the structure and complete amino acid sequence of IgG, a feat for which they were jointly awarded the 1972 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
[102] In a landmark series of experiments beginning in 1976, Susumu Tonegawa showed that genetic material can rearrange itself to form the vast array of available antibodies.
[citation needed] In clinical immunology, levels of individual classes of immunoglobulins are measured by nephelometry (or turbidimetry) to characterize the antibody profile of patient.
Antibodies directed against red blood cell surface antigens in immune mediated hemolytic anemia are detected with the Coombs test.
[107] Practically, several immunodiagnostic methods based on detection of complex antigen-antibody are used to diagnose infectious diseases, for example ELISA, immunofluorescence, Western blot, immunodiffusion, immunoelectrophoresis, and magnetic immunoassay.
[citation needed] New dioxaborolane chemistry enables radioactive fluoride (18F) labeling of antibodies, which allows for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of cancer.
[118] Anti-RhD antibodies are administered as part of a prenatal treatment regimen to prevent sensitization that may occur when a Rh-negative mother has a Rh-positive fetus.
Therefore, her humoral immune system will not make anti-Rh antibodies, and will not attack the Rh antigens of the current or subsequent babies.
[119] To obtain antibody that is specific for a single epitope of an antigen, antibody-secreting lymphocytes are isolated from the animal and immortalized by fusing them with a cancer cell line.
[citation needed] There are several ways to obtain antibodies, including in vivo techniques like animal immunization and various in vitro approaches, such as the phage display method.
Validation studies should at least include: The importance of antibodies in health care and the biotechnology industry demands knowledge of their structures at high resolution.
Common advantages over antibodies are better solubility, tissue penetration, stability towards heat and enzymes, and comparatively low production costs.
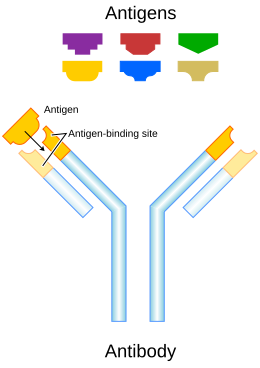



- Antibodies (A) and pathogens (B) free roam in the blood.
-
The antibodies bind to pathogens, and can do so in different formations such as:
- opsonization,
- neutralisation, and
- agglutination.
- A phagocyte (C) approaches the pathogen, and the Fc region (D) of the antibody binds to one of the Fc receptors (E) of the phagocyte.
- Phagocytosis occurs as the pathogen is ingested.