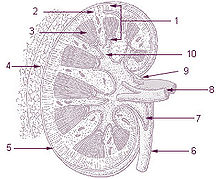
Cortex (anatomy)
[1] The word is of Latin origin and means bark, rind, shell or husk.
The cerebral cortex is typically described as comprising three parts: the sensory, motor, and association areas.
In addition, motor functions have been attributed to the posterior parietal cortex, which guides voluntary movements; and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which decides which voluntary movements to make according to higher-order instructions, rules, and self-generated thoughts.
The association areas of the human brain are highly developed, and are thought to play an integral role in complex functions.
[3] The parasensory association cortex receives signals from the primary sensory areas.