Cyclin-dependent kinase 2
[9] Original cell-culture based experiments demonstrated cell cycle arrest at the G1-S transition resulting from the deletion of Cdk2.
[10] Later experiments showed that Cdk2 deletions lengthened the G1 phase of the cell cycle in mouse embryo fibroblasts.
[10] Cells in Cdk2 knockout mice likely undergo fewer divisions, contributing to the reduction in body size.
[citation needed] This allows the glutamic acid located on the C-helix to form an ion pair with a nearby lysine side chain.
This triad (Lys 33, Glu 51 and Asp 145) is involved in ATP phosphate orientation and magnesium coordination, and is thought to be critical for catalysis.
This conformational change also relocates the activation loop to the C-lobe, revealing the ATP binding site now available for new interactions.
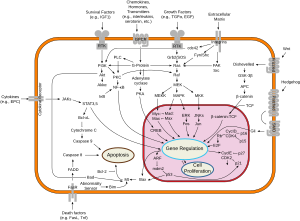
[18] This allows E2F transcription factors to express genes that promote entry into S phase where DNA is replicated prior to division.
[12] Pre-clinical models have shown preliminary success in limiting tumor growth, and have also been observed to reduce side effects of current chemotherapy drugs.
[12] Cdk1 is the only essential cyclin dependent kinase in the cell cycle, and inhibition could lead to unintended side effects.
Type II inhibitors target CDK2 in its unbound state, either occupying the ATP binding site or hydrophobic pocket within the kinase.
[24] Recently, the availability of new CDK crystal structures led to the identification of a potential allosteric binding site near the C-helix.
[30] Rosmarinic acid methyl ester is a plant-derived Cdk2 inhibitor, which was shown to suppress proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and to reduce neointima formation in mouse restenosis model.
[31] See also the PDB gallery below showing interactions with many inhibitors (inc Purvalanol B) In melanocytic cell types, expression of the CDK2 gene is regulated by the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor.