Cyclin-dependent kinase 4
[7] The gene is composed of 4,583 base pairs which together code for the 303 amino acid protein with a molecular mass of 33,730 Da.
[5][9][10] These two actions move the T-loop out of the active ATP-binding site and make ATP binding more favorable.
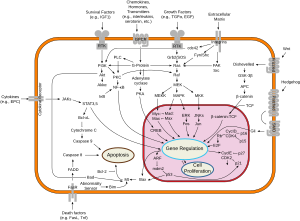
The older model proposes that the kinase is responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (Rb).
The Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) forms complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G1/S transition.
[5] As a kinase, the CDK4 serine/threonine active site converts ATP to ADP and transfers the removed phosphate group to Rb.
CDK4 may be able to directly phosphorylate transcription factors and co-regulators like Smad3, MYC, FOXM1, and MEP50 to regulate the cell cycle, survival and senescence.
Interestingly, CDK4-null mutant mice are viable, and in-vitro experiments show that cell proliferation is not significantly affected, likely due to compensatory roles played by other CDKs.
CDK activity is negatively regulated by cyclin kinase inhibitors (CKIs), which belong to one of two families.
Cell cycle regulation mechanisms called checkpoints, like G1/S, are in place to prevent this uncontrolled division.
This mutation was introduced also in animal models and its role as a cancer driver oncogene was studied thoroughly.
Cyclin D and CDK4/6 activities are observed to be up-regulated in certain cancers, sparking interest in the development of small-molecule inhibitors of CDK4/6.
Ribociclib are US FDA approved CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors for the treatment of estrogen receptor positive/ HER2 negative advanced breast cancer.