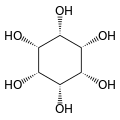
Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol
All these compounds are sometimes called inositol, although this name (especially in biochemistry and related sciences) most often refers to a particular isomer, myo-inositol, which has many important physiological roles and medical uses.
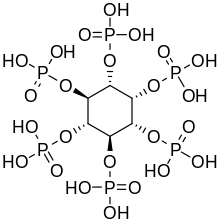
[2] These compounds form several esters with biochemical and industrial importance, such as phytic acid and phosphatidylinositol phosphate, The nine stereoisomers of cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol are distinguished by prefixes: myo-, scyllo-, muco-, D-chiro-, L-chiro-, neo-, allo-, epi-, and cis-inositol.
The relative stability of the two forms varies with the isomer, generally favoring the conformation where the hydroxyls are farthest apart from each other.
[4] There is a clear correlation between the melting points and the number and type of chains of hydrogen-bonded hydroxyls.
[9] Small amounts of myo-inositol are then converted by a specific epimerase to D-chiro-inositol,[10] which is an important messenger molecule in insulin signaling.
[11] A 2020 study found detectable amounts of epi-, neo-, chiro-, scyllo-, and myo-inositol in the urine of women, pregnant or not.