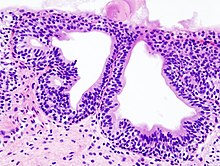
Cystitis glandularis
They undergo glandular metaplasia, a process in which irritated tissues take on a different form, in this case that of a gland.
They must distinguish a benign metaplastic change from the cancerous condition urothelial cell carcinoma.
Individuals with diffuse intestinal-type cystitis glandularis are at increased risk for developing bladder cancer.
[citation needed] Cystitis glandularis arises from and merges with Von Brunn's nests, which are groups of urothelial cells (cells of urinary tract) within the lamina propria and submucosa, formed from budding from the surface mucosa.
Other metaplastic entities in the urinary bladder include squamous metaplasia and nephrogenic adenoma.