Table (information)
A table is an arrangement of information or data, typically in rows and columns, or possibly in a more complex structure.
Tables appear in print media, handwritten notes, computer software, architectural ornamentation, traffic signs, and many other places.
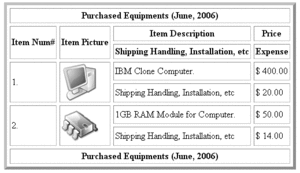
In books and technical articles, tables are typically presented apart from the main text in numbered and captioned floating blocks.
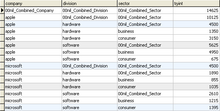
Certain considerations follow from this simplified description: The elements of a table may be grouped, segmented, or arranged in many different ways, and even nested recursively.
This structure is typically visually presented with an appropriate number of white spaces in front of each stub's label.
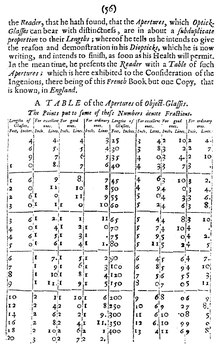
[9] They can condense large amount of information to a limited space and therefore they are popular in scientific literature in many fields of study.
As a communication tool, a table allows a form of generalization of information from an unlimited number of different social or scientific contexts.
[11][13] At a programming level, software may be implemented using constructs generally represented or understood as tabular, whether to store data (perhaps to memoize earlier results), for example, in arrays or hash tables, or control tables determining the flow of program execution in response to various events or inputs.