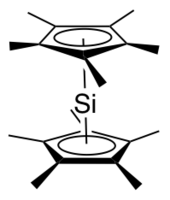
Decamethylsilicocene
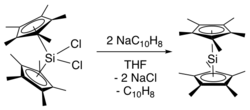
Generation of the sterically crowded bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)silicon(IV) dichloride required several steps, beginning with double deprotonation of (C5Me4H)2SiCl2 using tert-butyllithium, followed by treatment of the resultant (C5Me4Li)2SiCl2 with methyl iodide.
[4] This synthetic route avoids the synthesis of the bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)silicon(IV) dichloride starting material.
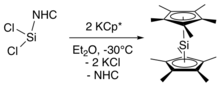
In this synthesis, the NHC-stabilized silylene (NHC=C[N−(C6H3–2,6–iPr2)CH]2) was treated with the potassium salt of pentamethylcyclopentadiene at −30 °C (−22 °F), followed by extraction of decamethylsilicocene into hexane at −60 °C (−76 °F) to remove the NHC and KCl byproducts.
[2][1] The major isomer adopts a Cs geometry reminiscent of a bent metallocene, with the cyclopentadienyl planes forming an angle of about 25° and the methyl groups staggered.
The minor isomer adopts a D5d geometry, the same as decamethylferrocene, with the cyclopentadienyl rings parallel to one another and the methyl groups staggered.
[5] NBO calculations are consistent with the predictions from a qualitative molecular orbital diagram, showing antibonding character between the silicon and the cyclopentadienyl ligands in both the HOMO and the LUMO.
Additionally, the pentamethylcyclopentadienylsilicon(II) cation can react with metal precursors to generate complexes with metal-silicon multiple bonds.