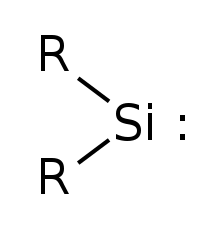
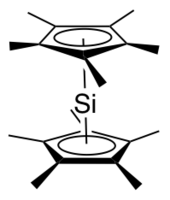
Silylene
Due to presence of a vacant p orbital, silylene rapidly reacts in a bimolecular manner[clarification needed] when condensed.
[5] Silylenes are generally synthesized by thermolysis or photolysis of polysilanes, by silicon atom reactions (insertion, addition or abstraction), by pyrolysis of silanes, or by reduction of 1,1-dihalosilane.
It has long been assumed that the conversion of metallic Si to tetravalent silicon compounds proceeds via silylene intermediates: Similar considerations apply to the direct process, the reaction of methyl chloride and bulk silicon.
The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two microseconds.
Added methanol acts as a chemical trap with a second order rate constant of 1.3×1010 mol−1 s−1 which is close to diffusion control.