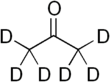
Deuterated acetone
Deuterated acetone ((CD3)2CO), also known as acetone-d6, is a form (isotopologue) of acetone (CH3)2CO in which the hydrogen atom (H) is replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope (2H or D).
Deuterated acetone is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
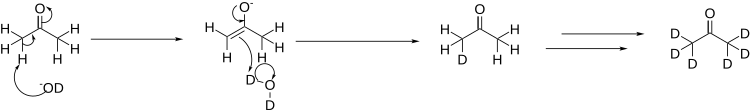
In this case, the base used is deuterated lithium hydroxide:[1] In order to fully deuterate the acetone, the process is repeated several times, distilling off the acetone from the heavy water, and re-running the reaction in a fresh batch of heavy water.
This article about an organic compound is a stub.
You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.This nuclear magnetic resonance–related article is a stub.