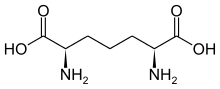
Diaminopimelic acid
meso-α,ε-Diaminopimelic acid is the last intermediate in the biosynthesis of lysine and undergoes decarboxylation by diaminopimelate decarboxylase to give the final product.
[1] DAP is a characteristic of certain cell walls[2] of some bacteria.
DAP is often found in the peptide linkages of NAM-NAG chains that make up the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria.
When in deficiency, they still grow but with the inability to make new cell wall peptidoglycan.
This is also the attachment point for Braun's lipoprotein.