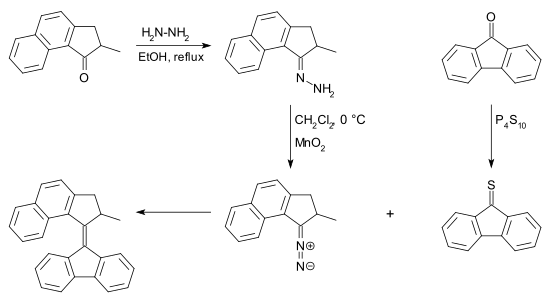
Barton–Kellogg reaction
Triphenylphosphine reacts as a nucleophile, opening the three-membered ring to form a sulfaphosphatane.
In a manner similar to the Wittig reaction, this structure then expels triphenylphosphine sulfide to produce an alkene.
The diazo compound can be obtained from a ketone by reaction with hydrazine to a hydrazone followed by oxidation.
Many reagents exist for this conversion for example silver(I) oxide and (bis(trifluoroacetoxy)iodo)benzene.
[7] The thioketone required for this reaction can be obtained from a ketone and phosphorus pentasulfide.