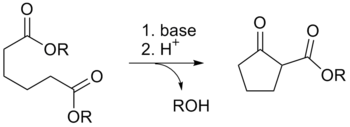Dieckmann condensation
The Dieckmann condensation is the intramolecular chemical reaction of diesters with base to give β-keto esters.
[1] It is named after the German chemist Walter Dieckmann (1869–1925).
Protonation with a Brønsted-Lowry acid (H3O+ for example) re-forms the β-keto ester.
[5] Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed.
1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.