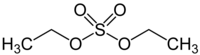
Diethyl sulfate
In preparing ethyl esters of fatty acids, both equivalents of the ethyl electrophile are transferred, unlike the usual alkylation of phenoxides:[1] Both dimethyl sulfate and diethyl sulfate react with inorganic nucleophiles as well.
The reaction of oleum with diethyl ether results in excessive oxidation of the ethyl groups.
[6] Experimentation with animals has suggested this compound is likely carcinogenic to humans as it was implicated in the development of laryngeal cancer.
[7] Evidence of the effects of this chemical compound on reproductive or developmental health is also lacking.
[8] Dialkyl sulfates can be rendered nontoxic by treatment with aqueous ammonia.