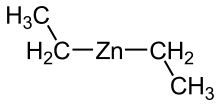Diethylzinc
Diethylzinc (C2H5)2Zn, or DEZ, is a highly pyrophoric and reactive organozinc compound consisting of a zinc center bound to two ethyl groups.
It is used in organic synthesis as a source of the ethyl carbanion in addition reactions to carbonyl groups.
[9] Additionally, it is commonly used in combination with diiodomethane as a Simmons-Smith reagent to convert alkenes into cyclopropyl groups.
Diethylzinc was also investigated by the United States Library of Congress as a potential means of mass deacidification of books printed on wood pulp paper.
Most infamously, the final prototype suffered damage in a series of diethylzinc explosions from trace amounts of water vapor in the chamber.
This led the authors of the study to humorously comment: It has also been established that tight or loose packing of books; the amount of alkaline reserve; reactions of DEZ with degradation products, unknown paper chemicals and adhesives; phases of the moon and the positions of various planets and constellations do not have any influence on the observed adverse effects of DEZ treatment.