Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase
[9] Additionally, DLD is a flavoenzyme oxidoreductase that contains a reactive disulfide bridge and a FAD cofactor that are directly involved in catalysis.
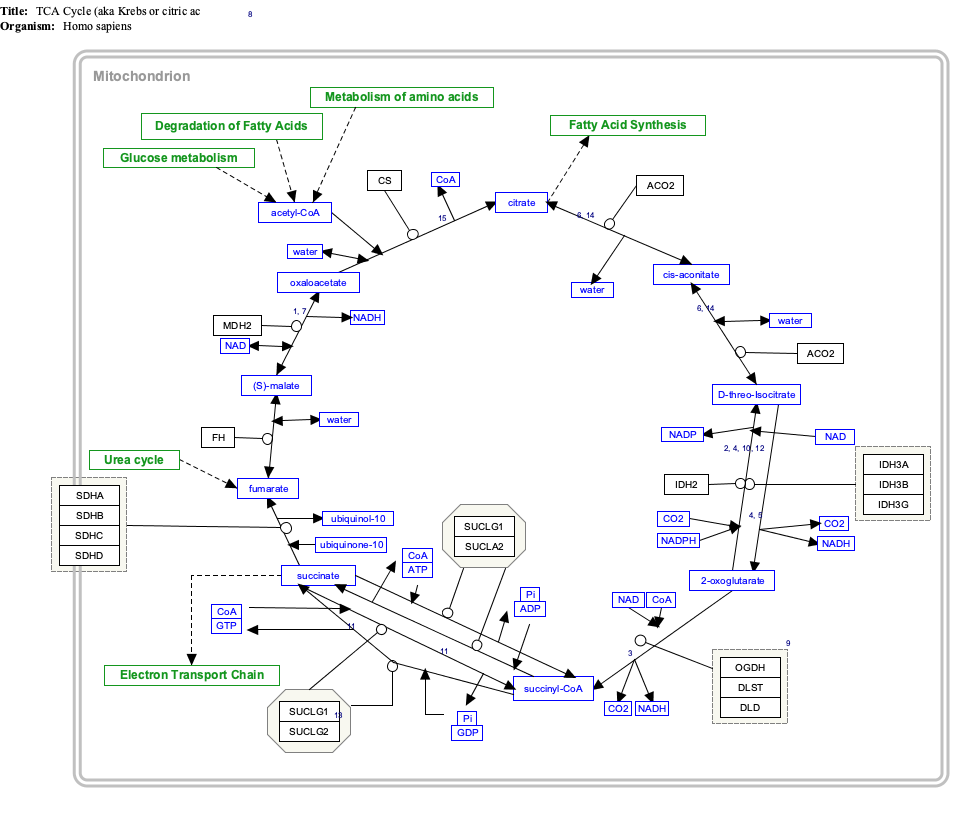
[13] The DLD homodimer functions as the E3 component of the pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, α-adipate and branched-chain amino acid-dehydrogenase complexes and the glycine cleavage system, all in the mitochondrial matrix.
[9] DLD is thought to have a pro-oxidant role by reducing oxygen to a superoxide or ferric to ferrous iron, which then catalyzes production of hydroxyl radicals.
[15][16] Diaphorase activity of DLD may have an antioxidant role through its ability to scavenge nitric oxide and to reduce ubiquinone to ubiquinol.
[21][22] In humans, mutations in DLD are linked to a severe disorder of infancy with failure to thrive, hypotonia, and metabolic acidosis.