Magnesium
Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table) it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2.
It reacts readily with air to form a thin passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal.
In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus.
Magnesium compounds are used medicinally as common laxatives and antacids (such as milk of magnesia), and to stabilize abnormal nerve excitation or blood vessel spasm in such conditions as eclampsia.
One hint is that it tarnishes slightly when exposed to air, although, unlike the heavier alkaline earth metals, an oxygen-free environment is unnecessary for storage because magnesium is protected by a thin layer of oxide that is fairly impermeable and difficult to remove.
[20] Direct reaction of magnesium with air or oxygen at ambient pressure forms only the "normal" oxide MgO.
[20] When submerged in water, hydrogen bubbles form slowly on the surface of the metal; this reaction happens much more rapidly with powdered magnesium.
Azo violet dye can also be used, turning deep blue in the presence of an alkaline solution of magnesium salt.
The addition of about one in three hundred parts arsenic reduces the corrosion rate of magnesium in a salt solution by a factor of nearly ten.
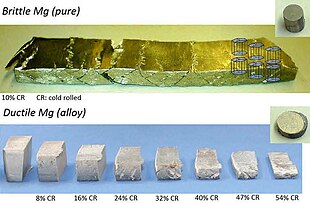
[26][27] Magnesium's tendency to creep (gradually deform) at high temperatures is greatly reduced by alloying with zinc and rare-earth elements.
The slope of the isochron has no age significance, but indicates the initial 26Al/27Al ratio in the sample at the time when the systems were separated from a common reservoir.
Magnesium is the eighth-most-abundant element in the Earth's crust by mass and tied in seventh place with iron in molarity.
[34] Although magnesium is found in more than 60 minerals, only dolomite, magnesite, brucite, carnallite, talc, and olivine are of commercial importance.
Since the Chinese mastery of the Pidgeon process the US market share is at 7%, with a single US producer left as of 2013: US Magnesium, a Renco Group company located on the shores of the Great Salt Lake.
[43][44] The Pidgeon method is less technologically complex and because of distillation/vapour deposition conditions, a high purity product is easily achievable.
[44] This process does have its share of disadvantages including production of harmful chlorine gas and the overall reaction being very energy intensive, creating environmental risks.
[45] The Pidgeon process is more advantageous regarding its simplicity, shorter construction period, low power consumption and overall good magnesium quality compared to the electrolysis method.
A saline solution containing Mg2+ ions is first treated with lime (calcium oxide) and the precipitated magnesium hydroxide is collected: The hydroxide is then converted to magnesium chloride by treatment with hydrochloric acid and heating of the product to eliminate water: The salt is then electrolyzed in the molten state.
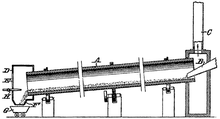
The chemistry is as follows: C + MgO → CO + Mg A disadvantage of this method is that slow cooling the vapour can cause the reaction to quickly revert.
In the commercial aerospace industry, magnesium was generally restricted to engine-related components, due to fire and corrosion hazards.
The general strategy for such alloys is to form intermetallic precipitates at the grain boundaries, for example by adding mischmetal or calcium.
[74] Because of low density and good mechanical and electrical properties, magnesium is used for manufacturing of mobile phones, laptop and tablet computers, cameras, and other electronic components.
[76] When burning in air, magnesium produces a brilliant white light that includes strong ultraviolet wavelengths.
This property was used in incendiary weapons during the firebombing of cities in World War II, where the only practical civil defense was to smother a burning flare under dry sand to exclude atmosphere from the combustion.
[98] Magnesium reacts with haloalkanes to give Grignard reagents, which are used for a wide variety of organic reactions forming carbon–carbon bonds.
Increased magnesium lowers calcium[114] and can either prevent hypercalcemia or cause hypocalcemia depending on the initial level.
[114] Both low and high protein intake conditions inhibit magnesium absorption, as does the amount of phosphate, phytate, and fat in the gut.
[118] Magnesium concentrations in plasma or serum may be monitored for efficacy and safety in those receiving the drug therapeutically, to confirm the diagnosis in potential poisoning victims, or to assist in the forensic investigation in a case of fatal overdose.
Chronically low serum magnesium levels are associated with metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus type 2, fasciculation, and hypertension.
Magnesium deficiency in plants causes late-season yellowing between leaf veins,[133] especially in older leaves, and can be corrected by either applying epsom salts (which is rapidly leached), or crushed dolomitic limestone, to the soil.