Edible frog
It is used for food, particularly in France as well as Germany and Italy, for the delicacy frog legs.
The edible frog is introduced in Spain,[4] Norway[5] and the United Kingdom.
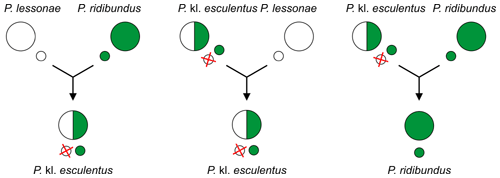
[9][10][12] The hybrid populations are usually propagated by mating (backcrosses) with a sympatric parental species – P. lessonae (LL) or P. ridibundus (RR) – providing the second, discarded parental genome (L or R respectively).
[13][11][12] For example, in the most widespread so called L–E system, edible frogs Pelophylax kl.
[9][12] Because this hybrid requires another taxon as a sexual host to reproduce, usually one of the parental species, it is a klepton,[14][15][16] hence the addition of the "kl."