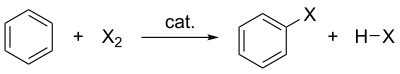
Electrophilic halogenation
In a series of studies, the powerful reagent obtained by using a mixture of iodine and potassium iodate dissolved in concentrated sulfuric acid was used.
In these studies both the kinetics of the reaction and the preparative conditions for the iodination of strongly deactivated compounds, such as benzoic acid and 3-nitrobenzotrifluoride, were investigated.
[3][4] While electrophilic fluorination is possible with F2/N2 (10%), XeF2, or N-F reagents like Selectfluor, these methods are seldom used, due to the formation of isomeric mixtures and polyfluorination products.
[5] Although mixtures also form in the case of other aromatic halogenations, fluoroaromatics are often extremely challenging to separate from their nonfluorinated, polyfluorinated, and/or isomeric counterparts.
In contrast, when the reactant is 2-phenylethylamine, it is possible to employ relatively apolar solvents with exclusive ortho- regioselectivity due to the intermediate formation of a chloramine, enabling the Intramolecular reaction.