Electrical engineering
The tools and equipment that an individual engineer may need are similarly variable, ranging from a simple voltmeter to sophisticated design and manufacturing software.
In 1762 Swedish professor Johan Wilcke invented a device later named electrophorus that produced a static electric charge.
[3] In 1782, Georges-Louis Le Sage developed and presented in Berlin probably the world's first form of electric telegraphy, using 24 different wires, one for each letter of the alphabet.
[8] By the end of the 19th century, the world had been forever changed by the rapid communication made possible by the engineering development of land-lines, submarine cables, and, from about 1890, wireless telegraphy.
In 1882, Thomas Edison switched on the world's first large-scale electric power network that provided 110 volts—direct current (DC)—to 59 customers on Manhattan Island in New York City.
In 1884, Sir Charles Parsons invented the steam turbine allowing for more efficient electric power generation.
In his classic physics experiments of 1888, Heinrich Hertz proved Maxwell's theory by transmitting radio waves with a spark-gap transmitter, and detected them by using simple electrical devices.
In 1895, Guglielmo Marconi began work on a way to adapt the known methods of transmitting and detecting these "Hertzian waves" into a purpose-built commercial wireless telegraphic system.
Marconi later transmitted the wireless signals across the Atlantic between Poldhu, Cornwall, and St. John's, Newfoundland, a distance of 2,100 miles (3,400 km).
[22] Millimetre wave communication was first investigated by Jagadish Chandra Bose during 1894–1896, when he reached an extremely high frequency of up to 60 GHz in his experiments.
[25][26] In 1897, Karl Ferdinand Braun introduced the cathode-ray tube as part of an oscilloscope, a crucial enabling technology for electronic television.
Two years later, Robert von Lieben and Lee De Forest independently developed the amplifier tube, called the triode.
In 1943, Tommy Flowers designed and built the Colossus, the world's first fully functional, electronic, digital and programmable computer.
[41] The earliest experimental MOS IC chip to be fabricated was built by Fred Heiman and Steven Hofstein at RCA Laboratories in 1962.
Power & Energy engineering deals with the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity as well as the design of a range of related devices.
In many regions of the world, governments maintain an electrical network called a power grid that connects a variety of generators together with users of their energy.
Telecommunications engineering focuses on the transmission of information across a communication channel such as a coax cable, optical fiber or free space.
For example, in an automobile with cruise control the vehicle's speed is continuously monitored and fed back to the system which adjusts the motor's power output accordingly.
[60] Later, in post-war years, as consumer devices began to be developed, the field grew to include modern television, audio systems, computers, and microprocessors.
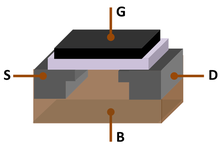
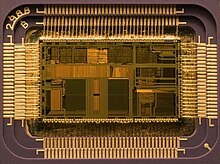
By contrast, integrated circuits packed a large number—often millions—of tiny electrical components, mainly transistors,[70] into a small chip around the size of a coin.
For example, flight instruments measure variables such as wind speed and altitude to enable pilots the control of aircraft analytically.
[86] The term mechatronics is typically used to refer to macroscopic systems but futurists have predicted the emergence of very small electromechanical devices.
The bachelor's degree generally includes units covering physics, mathematics, computer science, project management, and a variety of topics in electrical engineering.
An engineer's work must also comply with numerous other rules and regulations, such as building codes and legislation pertaining to environmental law.
The IEEE claims to produce 30% of the world's literature in electrical engineering, has over 360,000 members worldwide and holds over 3,000 conferences annually.
Membership and participation in technical societies, regular reviews of periodicals in the field and a habit of continued learning are therefore essential to maintaining proficiency.
For instance, medical electronics designers must take into account that much lower voltages than normal can be dangerous when electrodes are directly in contact with internal body fluids.
A lot of time may also be spent on tasks such as discussing proposals with clients, preparing budgets and determining project schedules.
Electrical engineers may be found in the pristine lab environment of a fabrication plant, on board a Naval ship, the offices of a consulting firm or on site at a mine.
For instance, large particle accelerators such as CERN need electrical engineers to deal with many aspects of the project including the power distribution, the instrumentation, and the manufacture and installation of the superconducting electromagnets.