EZH2
4MI0, 4MI5, 5HYN, 5IJ8, 5IJ7214614056ENSG00000106462ENSMUSG00000029687Q15910Q61188NM_001203247NM_001203248NM_001203249NM_004456NM_152998NM_001146689NM_007971NP_001190176NP_001190177NP_001190178NP_004447NP_694543NP_001140161NP_031997Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is a histone-lysine N-methyltransferase enzyme (EC 2.1.1.43) encoded by EZH2 gene, that participates in histone methylation and, ultimately, transcriptional repression.
EZH2 is capable of mono-, di-, and tri-methylation of H3K27 and has been associated with a variety of biological functions, including transcriptional regulation in hematopoiesis, development, and cell differentiation.
[17][20] This transcriptionally repressive state is thought to be due to PRC2/EZH2-EED-mediated H3K27 methylation and subsequent recruitment of PRC1 which facilitates condensation of chromatin and formation of heterochromatin.
[17] In breast cancer cells, EZH2 has been demonstrated to activate NF-κB target genes, which are involved in responses to stimuli.
[18] H3K27me3 is involved in suppressing genes that promote differentiation, thus maintaining an undifferentiated state of B- and T-cells and playing an important role in regulating hematopoiesis.
[21][28] Phosphorylation of T492 has been suggested to disrupt contacts between human EZH2 and its binding partners in the PRC2 complex, thus hindering its catalytic activity.
[33] Both isoforms contain elements that have been identified as important for EZH2 function including the nuclear localization signal, the EED and SUZ12 binding sites as well as the conserved SET domain.
These methylated lysines are important in the control of mammalian gene expression and have a functional role in heterochromatin formation, X-chromosome inactivation and transcriptional regulation.
[36] SET methyltransferases depend on a S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) cofactor to act as a methyl donor for their catalytic activity.
SET domain proteins differ from other SAM-dependent methyltransferases in that they bind their substrate and SAM cofactor on opposite sides of the active site of the enzyme.
[37] EZH2 primarily catalyzes mono- and di-methylation of H3K27 but a clinically relevant mutation of residue tyrosine 641 to phenylalanine (Y641F) results in higher H3K27 tri-methylation activity.
[42] Importantly, the mutation of tyrosine 641 in the active SET domain to a number of different amino acids is a common feature of some B-cell lymphomas.
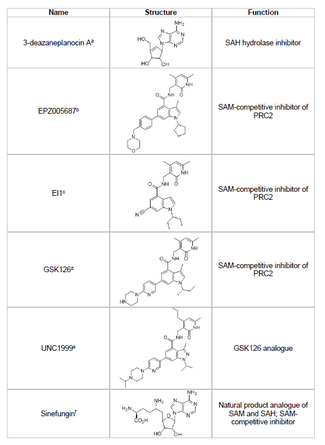
[43] Developing an inhibitor of EZH2 and preventing unwanted histone methylation of tumor suppressor genes is a viable area of cancer research.
[39] However, EZH2 and lysine methylation can have tumor suppressing activity, for example in myelodysplastic syndrome,[51] indicating that EZH2 inhibition may not be beneficial in all cases.
EZH2 is crucial for epigenetic regulation of specific patterning during osteochondrogenesis,[52] or bone and cartilage development, of the craniofacial skeletal elements.
By repressing inhibitors, EZH2 promotes bone and cartilage formation in facial skeletal features arising from the neural crest.
But in 2013, a study performed by Zhaomei Mu and his associates concluded that the knockdown gene for EZH2 inhibited both the migration and invasion of IBC cells.
[53] Mutations in the EZH2 gene have been linked with Weaver syndrome, a rare disorder characterized by advanced bone age, macrocephaly, and hypertelorism.
[14] The histidine residue in the active site of the wild-type EZH2 was mutated to tyrosine in patients diagnosed with Weaver syndrome.