Epothilone
Due to their better water solubility, cremophors (solubilizing agents used for paclitaxel which can affect cardiac function and cause severe hypersensitivity) are not needed.
[5] Endotoxin-like properties known from paclitaxel, like activation of macrophages synthesizing inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide, are not observed for epothilone B.
At higher antimitotic concentrations, paclitaxel appears to act by suppressing microtubule detachment from centrosomes, a process that is normally activated during mitosis.
[11] Epothilone D, with the generic drug name utidelone, was approved in China in 2021 for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
[12][13] Utidelone has shown benefits in a phase III breast cancer trial when added to capecitabine.
[14] One synthetic analog, ixabepilone, was approved in October 2007 by the United States Food and Drug Administration for use in the treatment of aggressive metastatic or locally advanced breast cancer that no longer responds to currently available chemotherapies.
[16] Epothilone B, with the generic drug name patupilone, was proven to contain potent in vivo anticancer activities at tolerated dose levels in several human xenograft models.
[18] Results of a phase III trial with ixabepilone (BMS-247550) in combination with capecitabine in metastatic breast cancer have been announced (2007 – leading to FDA approval).
[19] Due to the high potency and clinical need for cancer treatments, epothilones have been the target of many total syntheses.
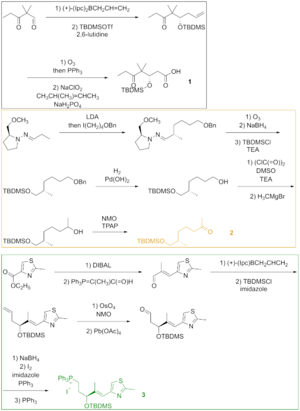
Ozonolysis, the last step of the Enders alkylation, was followed by reduction of the aldehyde and silylation of the resulting alcohol.
Thiazole 3 was synthesized from the ester, which was reduced with diisobutylaluminium hydride, and the aldehyde was reacted with the stabilized ylide in the Wittig reaction.
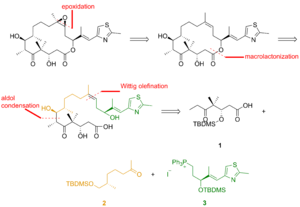
Epothilone B is a 16-membered polyketide macrolactone with a methylthiazole group connected to the macrocycle by an olefinic bond.
In this biosynthesis, both PKS and NRPS use carrier proteins, which have been post-translationally modified by phosphopantetheine groups, to join the growing chain.
PKS uses coenzyme-A thioester to catalyze the reaction and modify the substrates by selectively reducing the β carbonyl to the hydroxyl (Ketoreductase, KR), the alkene (Dehydratase, DH), and the alkane (Enoyl Reductase, ER).
The EPOS A contains a modified β-ketoacyl-synthase (malonyl-ACP decarboxylase, KSQ), an acyltransferase (AT), an enoyl reductase (ER), and an acyl carrier protein domain (ACP).