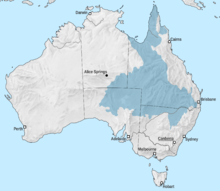
Eromanga Sea
[1][2] The sea covered large parts of what is now Queensland and Central Australia at least four times during the early Cretaceous.
[citation needed] The present-day Winton Formation represents remnants of the river plains that filled the basin left by the Eromanga Sea.
The Great Artesian Basin (GAB) was flooded by the Eromanga Sea and filled with volcaniclastic sediments eroded from the Cordillera's volcanic arc.
However the abundance of iron-rich and organic sediments have led to an anoxic sub-seafloor well-suited for anaerobic, pyrite-producing bacteria.
It was suggested that during the periods of uplift, erosion, and denudation opals were formed due to acidic oxidative weathering during 97 to 60 Ma.