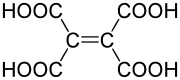
Ethylenetetracarboxylic acid
Ethylenetetracarboxylic acid is an organic compound with formula C6H4O8, or (HO(OC)-)2C=C(-(CO)OH)2.
By removal of four protons, the acid yields the anion C6O4−8, ethylenetetracarboxylate, which is one of the oxocarbon anions (consisting solely of oxygen and carbon).
By loss of 1 through 3 protons, it forms the anions C6H3O−8, C6H2O2−8, and C6HO3−8, called respectively trihydrogen-, dihydrogen-, and hydrogenethylenetetracarboxylate.
The acid can be obtained by hydrolysis of tetraethyl ethylenetetracarboxylate, which in turn can be obtained from diethyl dibromomalonate with sodium iodide.
[1] Ethylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride, a twofold acid anhydride of this compound, can be formed by direct dehydration at high temperature.