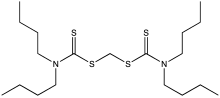
Extreme pressure additive
The sulfur or chlorine compounds contained in them can react with water and combustion byproducts, forming acids that facilitate corrosion of the engine parts and bearings.
In cutting fluids, their role is largely confined to formulations for forming complex stainless steel parts.
Oil-soluble organophosphates, with or without zinc, have excellent high-pressure and antiwear properties, and provide corrosion protection especially in presence of chlorinated hydrocarbons.
Zinc dialkyldithiophosphates (ZDDP) start decomposing at 130-170 °C, while the activation temperature of tricresyl phosphate (TCP) typically exceeds 200 °C.
Sulfur containing extreme pressure additives can cause corrosion problems in gears with parts made of bronze, brass and other copper alloy when high temperature environments are encountered.